[Deploy website]Introduction
Here is a step-by-step guide to deploying your Astro application using AWS S3 and CloudFront. This setup utilizes the AWS Cloudfront flat rate dustribution, which provides 1TB of data transfer and 10,000,000 requests per month on free tier.
Prerequisites
An AWS Account.
An Astro project ready to build.
AWS CLI installed (optional, but makes uploading easier)
[Phase 1]Prepare Your Astro Application
Astro builds static sites by default. Ensure your configuration is set to output static files.
Open
astro.config.mjsand ensure it looks like this:
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';
export default defineConfig({
output: 'static', // Default behavior
build: {
format: 'directory' // Generates about/index.html instead of about.html
}
});2. Build your project:
This creates a dist/ folder containing your website files.
npm run build[Phase 2]Create a Private S3 Bucket
We will create a private bucket. CloudFront will fetch content securely using Origin Access Control (OAC).
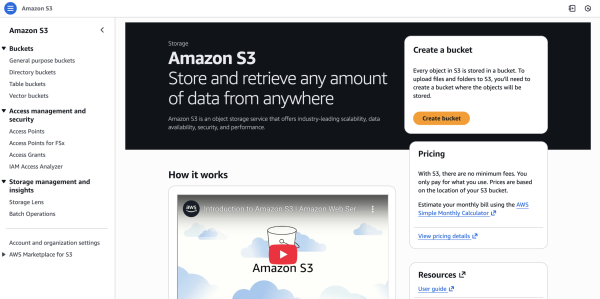
Go to the Amazon S3 Console and click Create bucket.
Bucket name: Give it a unique name (e.g.,
my-astro-site-2024).Region: Choose a region close to you (e.g.,
us-east-1).Block Public Access settings: Keep “Block all public access” CHECKED. (We do not want the bucket to be open to the world directly).
Click Create bucket.
Open your new bucket and click Upload. Drag and drop the contents of your
dist/folder (not the folder itself) into S3.
[Phase 3]Create a CloudFront Function (Crucial for Astro)
Since S3 is private, requesting your-site.com/about will fail because S3 looks for a file named about, but Astro created about/index.html. We need a tiny “URL Rewrite” function to fix this.
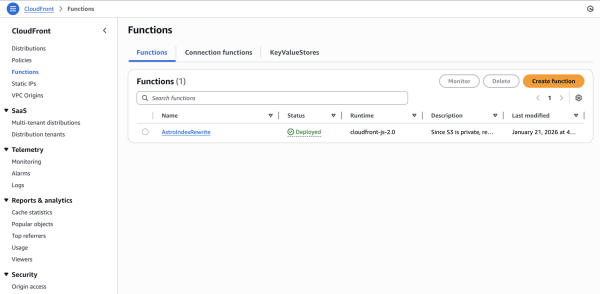
Go to the CloudFront Console -> Functions (on the left sidebar).
Click Create function.
Name:
AstroIndexRewrite.Runtime:
cloudfront-js-2.0.
Paste the following code:
Click Create function.
Name:
AstroIndexRewrite.Runtime:
cloudfront-js-2.0.
Paste the following code:
async function handler(event) {
var request = event.request;
var uri = request.uri;
// Check if the URI is missing a file name.
if (uri.endsWith('/')) {
request.uri += 'index.html';
}
// Check if the URI is missing a file extension.
else if (!uri.includes('.')) {
request.uri += '/index.html';
}
return request;
}4. Click Save changes and then Publish function.
[Phase 4]Create CloudFront Distribution
Go to CloudFront -> Distributions -> Create distribution.
- This will allow you to choose plan you required.
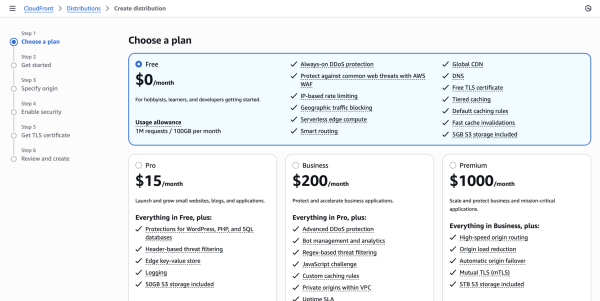
I choose free plan.
Add Distribution name
- Choose Distribution type.
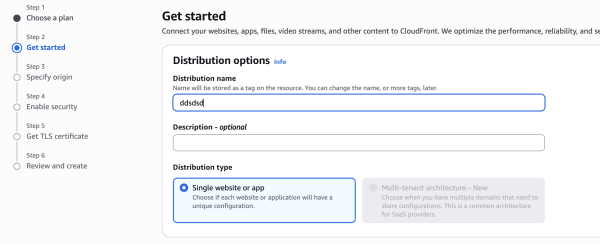
Origin domain: Click the input and select your S3 bucket from the list.
Origin access: Select “Origin access control settings (recommended)”.
Click Create control setting (keep defaults) and click Create.
Viewer protocol policy: Select “Redirect HTTP to HTTPS”.
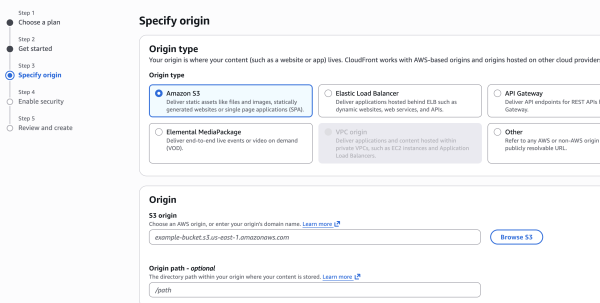
Web Application Firewall (WAF): Select “Do not enable security protections” (unless you want to pay extra for WAF).
Click Create distribution.
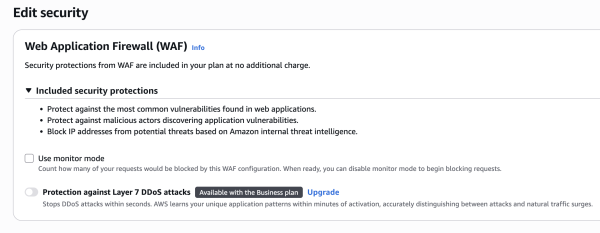
Function associations:
Scroll down to Viewer request.
Function type: CloudFront Function.
Function ARN: Select
AstroIndexRewrite(the function you made in Phase 3).
Web Application Firewall (WAF): Select “Do not enable security protections” (unless you want to pay extra for WAF).
Default root object: Type
index.html.Price Class: Use “Use all edge locations (Best Performance)”. This is covered by the 1TB Free Tier.
Click Create distribution.
[phase 5]Grant CloudFront Permission to S3
After creating the distribution, you will see a blue banner at the top of the screen saying “The S3 bucket policy needs to be updated”.
Click Copy policy in that banner.
Go back to your S3 Bucket -> Permissions tab.
Scroll down to Bucket policy, click Edit, and paste the policy you copied.
It should look like this (but with your specific IDs):
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": {
"Sid": "AllowCloudFrontServicePrincipalReadOnly",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "cloudfront.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::YOUR_BUCKET_NAME/*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"AWS:SourceArn": "arn:aws:cloudfront::YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID:distribution/YOUR_DIST_ID"
}
}
}
}
Phase 6: Verify Deployment
Go to your CloudFront Distribution dashboard.
Copy the Distribution Domain Name (e.g.,
d12345abc.cloudfront.net).Open it in your browser.
Homepage should load.
Navigate to a sub-page (e.g.,
/about). It should load correctly without the.htmlextension thanks to the CloudFront Function.
[phase 6]Connect GoDaddy domain to CloudFront
Connecting your GoDaddy domain to CloudFront requires three distinct phases. You cannot simply point the DNS to CloudFront immediately; you must first prove you own the domain by generating a free SSL certificate in AWS.
Here is the step-by-step process.
Phase 1: Request a Free SSL Certificate (AWS)
CloudFront requires an SSL certificate to serve your custom domain (HTTPS).
Log in to the AWS Console and switch your region to US East (N. Virginia) us-east-1.
Critical: CloudFront only accepts certificates from this specific region.
Search for Certificate Manager (ACM).
Click Request. Select Request a public certificate and click Next.
Domain names: Enter your domain in two formats:
your-domain.com*.your-domain.com(covers www and others)
Validation method: Select DNS validation.
Click Request.
You will see a list of certificates. Click the Certificate ID you just created.
In the Domains section, you will see “CNAME name” and “CNAME value”. Keep this page open; you need these for GoDaddy.
Phase 2: Verify Ownership in GoDaddy
You must add the CNAME record from Phase 1 into GoDaddy to prove you own the domain.
Log in to GoDaddy -> Domain Portfolio.
Select your domain and click DNS -> Manage Zones (or “Edit DNS”).
Click Add New Record:
Type:
CNAMEName: Paste the CNAME name from AWS.
Note: GoDaddy auto-appends your domain. If AWS gives you
_12345.your-domain.com, only paste_12345into the Name field.
Value: Paste the CNAME value from AWS exactly as is.
TTL:
1 Hour.
Click Save.
Wait 5-10 minutes. Go back to the AWS Certificate Manager console. The status should change from “Pending validation” to “Issued”.
Phase 3: Connect CloudFront to Your Domain
Now that you have a certificate, you can tell CloudFront to use it.
Go to the CloudFront Console and click your Distribution ID.
Under General, click Edit.
Alternate Domain Names (CNAMEs): Click Add item and enter:
www.your-domain.comyour-domain.com
Custom SSL Certificate: Click the dropdown and select the certificate you created in Phase 1.
Scroll to the bottom and click Save changes.
Point GoDaddy to CloudFront
Now we send the actual traffic from GoDaddy to AWS. As discussed, we will use the www method because it is the most stable way to handle root domains on GoDaddy.
Step A: Point www to CloudFront
Go to your GoDaddy DNS Management page.
Look for an existing record with Name
www.If it exists: Click the Pencil icon to edit it.
If not: Click Add New Record and choose Type
CNAME.
Name:
wwwValue: Paste your CloudFront Distribution Domain Name (e.g.,
d12345abc.cloudfront.net).Tip: You can find this on the main CloudFront dashboard under “Domain Name”.
TTL:
1 Hour.Click Save.
Step B: Forward the Root Domain (@) This ensures that if someone types your-domain.com (without www), they don’t get an error.
Still in GoDaddy, scroll down to the section labeled Forwarding. (Sometimes it is a tab or a separate menu item called “Forwarding” depending on the GoDaddy interface version).
Look for Domain (not Subdomain) and click Add Forwarding.
Destination URL:
Select
https://from the dropdown.Enter:
www.your-domain.com
Forward Type:
Permanent (301).Settings: Select “Update my nameservers and DNS settings to support this change” (if asked).
Click Save.
Part 3: Final Verification
It usually takes about 15 to 30 minutes for these changes to propagate across the internet.
Open a new browser tab (incognito mode is best to avoid caching).
Type
www.your-domain.com-> It should load your Astro site securely with the lock icon.Type
your-domain.com-> It should automatically flip towwwand load your site.
